In recent years, with the increasing awareness of environmental protection, people’s pursuit of goals has also changed. Nowadays, most people prefer to use safe, green, and pollution-free renewable bio based materials to replace traditional petroleum based materials. Among them, polylactic acid is widely used, which is basically ubiquitous. In our daily lives, shopping bags, paper cups, lunch boxes, straws, and so on in supermarkets. Below, let’s talk about the knowledge of polylactic acid.
What is PLA?
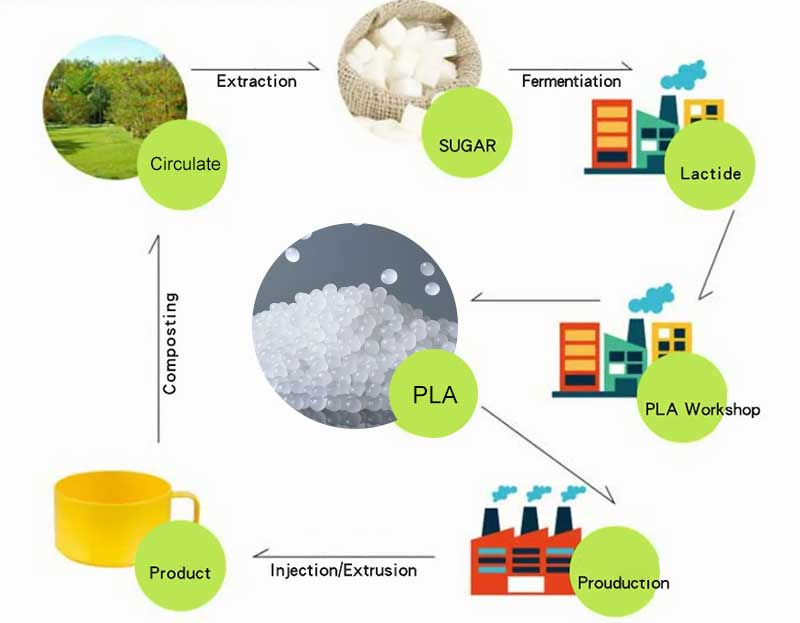
PLA, also known as Polyactive Acid, is a polymer material synthesized from lactic acid produced by corn fermentation. It has excellent biodegradability and is suitable for products and fields such as straws, tableware, film packaging materials, fibers, fabrics, 3D printing materials, etc. It also has great development potential in fields such as medical auxiliary materials, automotive parts, agriculture, forestry, and environmental protection. Due to its biodegradability, it also has a profound impact on environmental protection.
The traditional methods of plastic disposal mainly include recycling, landfill, and incineration. Among them, repeated recycling leads to a decrease in the performance of plastics, while landfill and incineration inevitably lead to various long-term and deep-seated environmental problems. After being discarded, polylactic acid products can not only undergo composting and degradation treatment, but also be suitable for other traditional solid waste treatment methods. Composting refers to the process of organic decomposition of garbage under artificially controlled conditions through the biochemical action of microorganisms. Compared to other methods of garbage treatment, composting has the advantages of green and environmental protection. After the disposal of our sound field’s polylactic acid products, they can be 100% degraded by microorganisms, generating carbon dioxide and water to return to nature.
However, the biodegradability of PLA is not unconditional. The biodegradation of PLA requires two basic conditions: a humidity of 50% -60% and a temperature of 50-70 degrees Celsius. Under these conditions, microorganisms are likely to undergo months or even longer to gradually decompose PLA.
In addition to PLA, we can also provide biodegradable PBAT PBS PBSA PBST

Polylactic acid originates from the natural and fully soluble properties, driving the formation of a regeneration cycle system for biomass resources; From the perspective of raw materials, PLA’s raw materials are lactic acid fermented from sugar extracted from crops such as corn, sugarcane, and sugar beets through deep processing; From the perspective of product disposal. PLA products can be degraded into carbon dioxide and water, and participate in biological regeneration and cycling processes again through crop photosynthesis. The entire process from production to degradation of PLA fully demonstrates that PLA originates from nature and belongs to nature.
At the same time, polylactic acid has good biocompatibility and degradability, making it a crystalline thermoplastic material with relatively high thermal stability. Suitable for injection molding, extrusion, spinning and other processing processes, the processed products can be widely used in various fields such as home furnishings, tableware, packaging, clothing, agriculture, electronic products, etc. It can be seen that PLA degradable plastics will be a development trend in the future. If you would like to learn more information, please contact us.