Titanium alkoxides are a group of organometallic compounds widely used in coatings, catalysts, sol-gel processes, and the production of titanium dioxide (TiO₂). Among them, Titanium(IV) Butoxide (CAS 5593-70-4)—also known as Tetrabutyl titanate or Tetra-n-butyl orthotitanate—is one of the most important and commonly applied.
While all titanium alkoxides share a similar backbone, their different alkyl groups give them unique chemical and industrial properties. This article explores the key differences between Titanium(IV) butoxide and other titanium alkoxides, helping industries and researchers understand which option best suits their needs.
I. What is Titanium(IV) Butoxide (CAS 5593-70-4)?
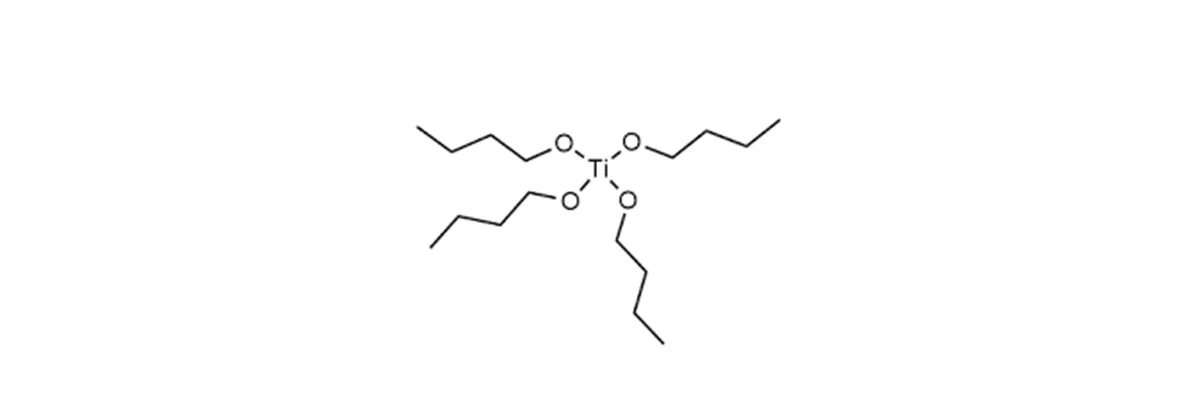
Titanium(IV) butoxide is an organotitanium compound with the molecular formula Ti(OC₄H₉)₄. It is typically a clear to pale yellow liquid that is sensitive to moisture and reacts readily with water through hydrolysis.
1. Key Points:
Chemical Name: Titanium(IV) butoxide
CAS Number: 5593-70-4
Synonyms: Tetrabutyl titanate, Tetra-n-butyl orthotitanate
Appearance: Clear to slightly yellow liquid
Properties: High reactivity, soluble in many organic solvents, controlled hydrolysis rate.
2. Main Applications:
As a precursor for titanium dioxide nanoparticles.
In sol-gel processing for coatings and thin films.
As a catalyst in esterification and transesterification reactions.
In the electronics industry for dielectric and optical coatings.
Because of its balance between reactivity and stability, Titanium(IV) butoxide is one of the most versatile titanium alkoxides used in both research and large-scale industrial production.
II. Common Types of Titanium Alkoxides
Titanium alkoxides form an important class of titanium-based chemicals where titanium is bonded to alkoxy groups (–OR). The properties and applications of these compounds vary significantly depending on the type of alkyl group, which directly affects their reactivity, stability, and suitability for industrial use. Below are the most common types of titanium alkoxides:
1. Titanium(IV) Butoxide (Tetrabutyl Titanate, CAS 5593-70-4)
Features: Moderate reactivity, relatively stable during storage, and offers controlled hydrolysis.
Applications: Widely used in coatings, adhesives, sol-gel processing, and as a precursor for TiO₂ nanoparticles.
Why popular: Its balance between reactivity and stability makes it suitable for both laboratory research and large-scale production.
2. Titanium(IV) Isopropoxide (TTIP)
Features: Much more reactive than butoxide, leading to faster hydrolysis and condensation.
Applications: Used in thin-film deposition (CVD and sol-gel methods), production of photocatalytic TiO₂, and electronics manufacturing.
Notes: Because of its higher reactivity, handling requires careful moisture control.
3. Titanium(IV) Ethoxide
Structure: Contains four ethoxy groups (C₂H₅O).
Features: Intermediate between methoxide and isopropoxide in terms of reactivity and stability.
Applications: High-purity material synthesis, optical coatings, and laboratory-scale research.
Notes: Often selected when purity and controlled reaction speed are critical.
4. Titanium(IV) Methoxide
Structure: Contains four methoxy groups (CH₃O).
Features: The smallest alkyl group gives it very high reactivity and the fastest hydrolysis rate.
Applications: Mostly limited to organic synthesis and specialized research due to handling difficulties.
Notes: Rare in industrial use because it is unstable in moist environments and difficult to store.

5. Mixed Titanium Alkoxides
In addition to the pure forms, mixed alkoxides—where different alkyl groups are bonded to titanium—are sometimes synthesized to fine-tune reactivity and solubility. These are used in specialized research and tailored industrial applications.
Common Titanium Alkoxides Comparison Table
| Titanium Alkoxide | Alkyl Group | CAS Number | Reactivity | Hydrolysis Rate | Stability |
| Titanium(IV) Butoxide | Butoxy (C₄H₉O) | 5593-70-4 | Moderate | Controlled/Slower | High |
| Titanium(IV) Isopropoxide (TTIP) | Isopropoxy (C₃H₇O) | 546-68-9 | High | Fast | Moderate |
| Titanium(IV) Ethoxide | Ethoxy (C₂H₅O) | 78-10-4 | Medium | Moderate | Moderate |
| Titanium(IV) Methoxide | Methoxy (CH₃O) | 108-32-7 | Very High | Very Fast | Low |
| Mixed Titanium Alkoxides | Mixed R groups | Various | Variable | Variable | Variable |
III. General Characteristics of Titanium Alkoxides
Across these types, titanium alkoxides share several important traits:
Moisture sensitivity: They hydrolyze rapidly in contact with water.
Sol-gel applications: All types are excellent precursors for TiO₂ thin films and nanoparticles.
Versatility: Depending on the alkyl group, they can be optimized for fast reactions or for stable, controlled processing.
Choice factors: The decision between Titanium(IV) butoxide (Tetrabutyl titanate) and other alkoxides usually depends on the balance needed between reactivity, processing conditions, and final application.
IV. Why Choose Titanium(IV) Butoxide?
There are several reasons industries often prefer Titanium(IV) butoxide (Tetrabutyl titanate):
Better process control: Slower hydrolysis makes it easier to manage in large-scale industrial settings.
Film-forming ability: Produces high-quality, uniform coatings.
Versatility: Works in multiple industries, from coatings to catalysts.
Availability: Widely supplied by global Tetrabutyl titanate suppliers.
For manufacturers seeking a balance of reactivity and stability, Titanium(IV) butoxide is often the most practical choice compared to other titanium alkoxides.
V. Reliable Tetrabutyl Titanate Suppliers
As a leading Tetrabutyl titanate supplier, we provide high-quality Titanium(IV) butoxide (CAS 5593-70-4) with consistent performance for industrial applications. When choosing a supplier, several factors are critical, and we ensure all are met:
High Purity: Our Titanium(IV) butoxide meets stringent purity standards, ensuring excellent performance in coatings, catalysts, and sol-gel processes.
Consistent Quality: We guarantee batch-to-batch consistency, so large-scale production remains stable and reliable.
Proper Packaging & Handling: Our products are packed in moisture-proof containers to prevent premature hydrolysis and maintain long-term stability.
Technical Support: As experienced Tetrabutyl titanate suppliers, we provide tailored solutions and technical guidance to meet your specific industrial requirements.
Partnering with us ensures you get top-quality Tetrabutyl titanate that minimizes production risks and delivers reliable results across coatings, catalysts, and advanced material applications.
VI. Conclusion
Titanium(IV) butoxide (CAS 5593-70-4) remains a preferred titanium alkoxide due to its controlled reactivity, excellent film-forming properties, and versatile industrial applications. While other titanium alkoxides such as isopropoxide and ethoxide have their specific uses, Tetrabutyl titanate is ideal for industries that require both stability and high performance.
As a trusted Tetrabutyl titanate supplier, we provide high-purity, consistent Titanium(IV) butoxide, backed by technical expertise and reliable supply.