Boron Oxide Powder (CAS 1303-86-2) is an essential inorganic chemical widely used in high-performance glass, ceramics, and metallurgical production. Known chemically as Boron Trioxide (B₂O₃), it plays a critical role in enhancing strength, thermal resistance, and chemical durability in numerous industrial materials.
As global demand for advanced materials continues to rise—especially in electronics, aerospace, and energy industries—Boron Oxide has become a core raw material for specialty glass and advanced ceramics manufacturing.
In this article, we explore the properties and key applications of Boron Oxide Powder and explain why selecting a reliable Boron Oxide Supplier is crucial for consistent quality and performance.
I. What Is Boron Oxide Powder?
Boron Oxide Powder is a white, amorphous chemical compound with excellent glass-forming ability and strong reactivity with metal oxides.
Chemical Details:
| ทรัพย์สิน | สเปค |
| สารเคมีชื่อ | Boron Oxide / Boron Trioxide |
| CAS | 1303-86-2 |
| ลองโมเลกุลองสูตร | B₂O₃ |
| รูปลักษณ์ | White crystalline or glassy powder |
| Key features | Low melting point, high thermal stability, strong fluxing ability |
Its ability to modify glass structure, reduce melting temperature, and improve mechanical strength makes it a strategic raw material in multiple industrial sectors.
II. Key Industrial Applications of Boron Oxide Powder
1. Glass Manufacturing & Borosilicate Glass Production
In glass production, Boron Oxide Powder serves as a glass network former and fluxing agent. Its primary role is to reduce the melting temperature of raw materials while increasing thermal and chemical resistance.
Borosilicate glass: Adding Boron Oxide creates highly heat-resistant glass ideal for laboratory equipment, cookware, and industrial glass.
Optical glass: Its inclusion improves transparency and minimizes thermal expansion, essential for precision lenses and optical instruments.
Glass fibers & fiberglass: Boron Oxide strengthens the glass matrix, improving tensile strength and resistance to thermal stress.
LCD and display glass: Ensures uniformity and stability, which is crucial for electronics applications.
In essence, Boron Oxide allows manufacturers to produce glass that can withstand extreme temperatures and harsh chemical environments without compromising clarity or strength.
2. Advanced Ceramic Materials
In ceramics, Boron Oxide Powder acts as a fluxing agent and sintering aid. It lowers the sintering temperature, enabling better densification and reducing energy costs during production.
Technical ceramics: Boron Oxide improves mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance, essential for aerospace components and industrial machinery.
Refractory materials: Enhances resistance to high temperatures, allowing ceramics to maintain shape and stability in furnaces or kilns.
Ceramic glazes & enamels: Promotes smooth, glossy surfaces with improved chemical durability.
Electronic ceramics: Boron Oxide ensures precise dielectric properties and thermal stability for capacitors and insulators.
By optimizing the microstructure, Boron Oxide Powder helps create ceramics with enhanced durability, longevity, and performance in demanding industrial applications.

3. Metallurgy and Metal Treatment
In metallurgical processes, Boron Oxide serves as a flux and additive, helping refine metals and improve alloy properties.
Steel production: Boron Oxide is added to produce boron steels, which are stronger, harder, and more corrosion-resistant.
Non-ferrous alloys: Acts as a flux to remove impurities during melting, ensuring cleaner, high-quality metal products.
Alloy refining: Enhances the hardness, toughness, and thermal stability of alloys used in automotive, aerospace, and defense industries.
Deoxidation processes: Reacts with oxygen to reduce oxidation, improving metal yield and overall quality.
The precise control of Boron Oxide content in metallurgical processes directly affects the performance and reliability of high-strength steels and advanced alloys.
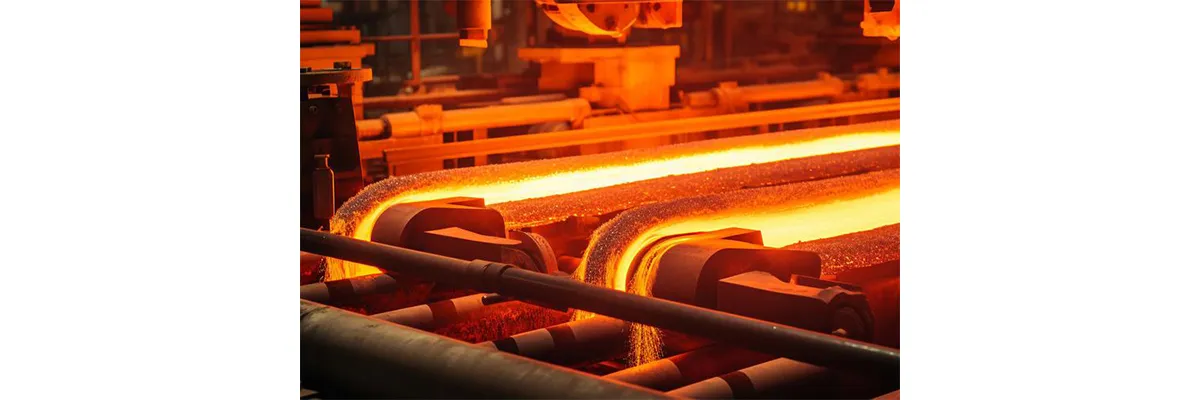

4. Other Applications
Beyond its main uses, Boron Oxide Powder also finds application in:
Catalysts and catalyst carriers: Boron Oxide supports active metal sites, enhancing catalytic efficiency.
Flame-retardant materials: Incorporated into polymers and composites to improve fire resistance.
Electronic and optical coatings: Provides thermal and chemical stability in protective coatings.
Composite materials: Improves bonding and performance of advanced composites for aerospace and energy industries.
Its versatility makes Boron Oxide an essential additive in multiple high-tech industrial fields.
III. Boron Oxide Price: What Factors Influence It?
Boron Oxide Price is affected by several factors:
- Purity and grade: Industrial grade vs. high-purity powder
- Raw material availability: Boron mineral sources impact cost
- Order size and packaging: Bulk orders often reduce per-unit cost
- Supply chain and logistics: International shipping and market demand fluctuations
Partnering with a reliable Boron Oxide Supplier ensures consistent quality and competitive pricing, reducing production risks.
IV. Why Choose Us as Your Boron Oxide Supplier
As a leading Boron Oxide Supplier, we provide high-quality Boron Oxide Powder (CAS 1303-86-2) with consistent purity and particle size. Our products are carefully manufactured and quality-controlled to meet the demanding requirements of glass, ceramics, and metallurgy industries.
V. สรุป
Boron Oxide Powder (CAS 1303-86-2) is an indispensable material in glass, ceramics, and metallurgy, offering exceptional thermal resistance, chemical stability, and mechanical strength. As a trusted Boron Oxide Supplier, we provide high-quality powder with consistent performance, competitive Boron Oxide Price, and reliable supply to meet your industrial needs.